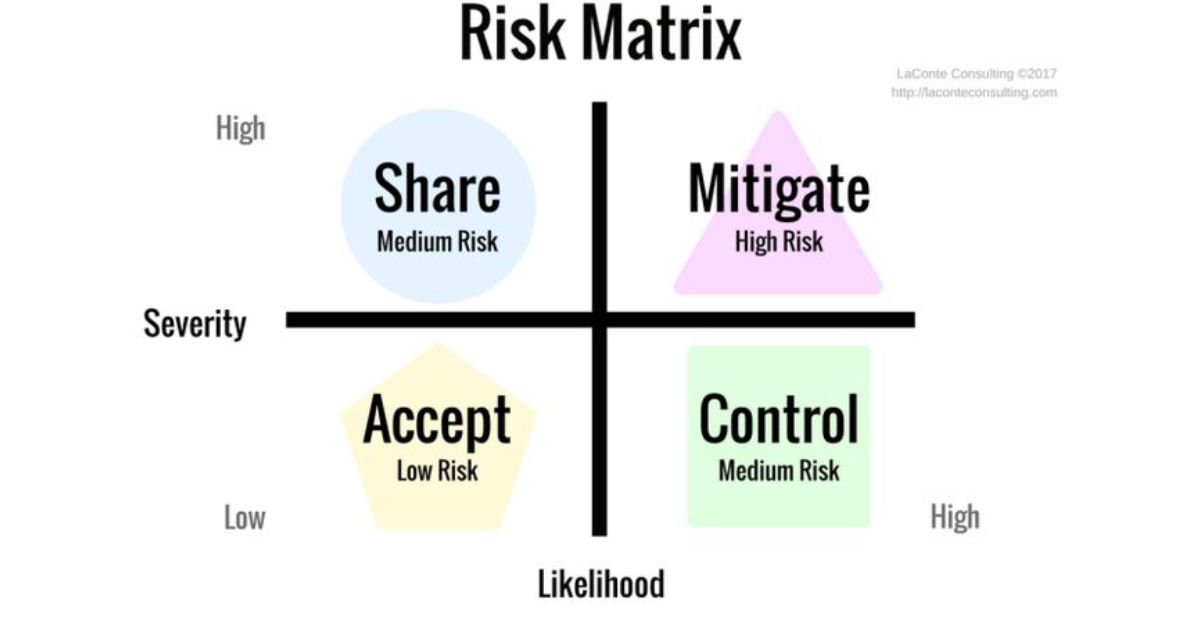
A risk matrix is a tool used to identify and evaluate risks in a clear, visual way. It helps organizations assess the likelihood and impact of various risks by plotting them on a grid. This grid usually features likelihood on one axis and severity on the other, creating a simple way to see how serious different risks are.
Understanding and using a risk matrix can make a big difference in how effectively you manage risks. Imagine being able to quickly see which risks need your immediate attention and which can be monitored with less urgency.
This tool can help you prioritize your actions and make more informed decisions about risk management. This article will explore key strategies for using a risk matrix effectively. It’ll walk you through the steps to create and utilize this tool, analyze risk levels, and develop management strategies.
What is a Risk Matrix?
A risk matrix is a visual tool used to assess and prioritize risks within an organization. It helps to map out potential risks by plotting them on a grid based on their likelihood and severity. This simple yet effective tool allows you to see at a glance which risks are most pressing and need immediate attention.
By organizing risks visually, you can quickly understand the overall risk landscape. Typically, a risk matrix is structured as a 5×5 grid. The Y-axis represents the likelihood of a risk occurring, while the X-axis shows the severity of the consequences.
Each risk is plotted according to where it falls on this grid, helping you determine its overall risk level. This clear structure makes it easier to categorize and prioritize risks systematically.
Also Read This: Discover Proven Wellness Tips on the //vital-mag.net Blog
Steps to Create and Use a Risk Matrix
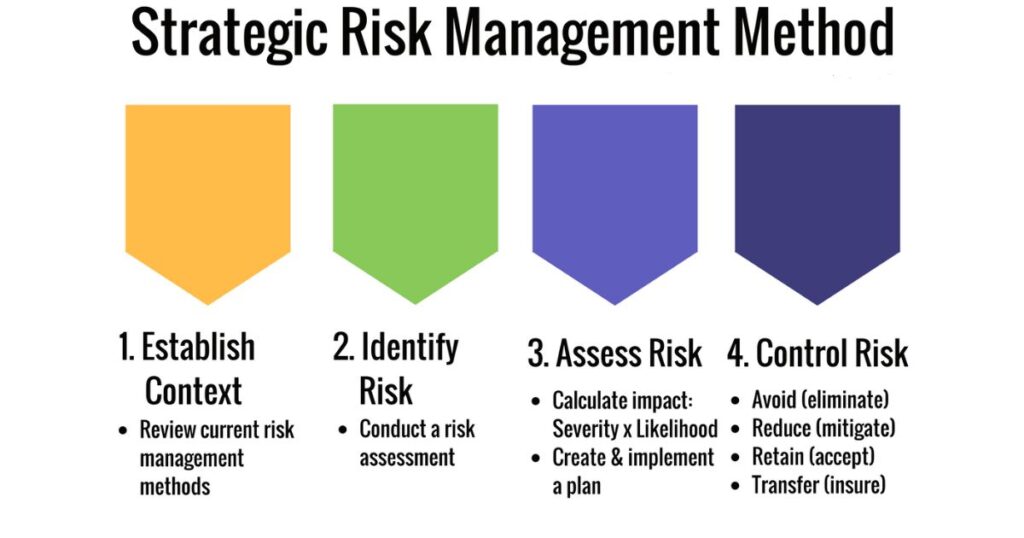
To create and use a risk matrix, start by identifying potential risks your organization may face. Evaluate each risk by determining its likelihood and severity, using clear criteria to assess both. Once evaluated, plot the risks on the matrix according to their likelihood on one axis and their potential impact on the other.
This gives a visual representation of which risks are more critical. Finally, use this matrix to prioritize risks and plan strategies to mitigate or manage them. Regularly update your matrix to keep your risk assessment current and effective.
1. Identify Risks
- List Potential Risks: Begin by listing all possible risks that could impact your organization. This includes operational, financial, strategic, and compliance risks. Ensure no significant risks are overlooked by considering various scenarios.
- Consider All Areas: Ensure that you cover all relevant areas and departments within your organization to get a comprehensive view of potential risks. A thorough risk inventory will provide a solid foundation for accurate assessment.
2. Evaluate Risks
- Assess Likelihood: Determine how likely each risk is to occur. Use categories such as ‘rare’, ‘unlikely’, ‘possible’, ‘likely’, and ‘certain’. This helps in understanding how often you might expect these risks to materialize.
- Assess Impact: Evaluate the severity of the consequences should the risk occur. Use categories like ‘very low’, ‘low’, ‘medium’, ‘high’, and ‘extreme’. This step helps to gauge how significant the impact of each risk would be on your organization.
3. Plot Risks on the Matrix
- Input Data: Place each risk on the grid based on its assessed likelihood and impact. This visual placement helps to clarify which risks are high, medium, or low. It makes it easier to see which risks need more attention.
- Visual Representation: The matrix provides a clear picture of where each risk falls in terms of severity and likelihood. This representation aids in making informed decisions about which risks to address first.
Analyze Risk Levels
After plotting the risks on the matrix, analyzing their levels becomes crucial for decision-making. High-risk areas (usually marked in red) require immediate action, while medium-risk (yellow) may need risk reduction strategies. Low-risk areas (green) are typically acceptable but should still be monitored.
Color coding helps you quickly identify the severity of each risk and prioritize actions accordingly. Understanding risk levels allows you to allocate resources and develop appropriate responses to mitigate the impact on your organization.
Also Read This: ARK: Survival Evolved (2017) Game Icons Banners
Color-Coding Risks
| Color | Risk Level | Description |
| Green | Low risk | Indicates low risk. These risks are typically manageable with minimal intervention. They represent areas where normal monitoring is sufficient. |
| Yellow/Orange | Medium risk | Represents medium risk. These risks may require mitigation strategies to reduce potential impact. They call for targeted actions to manage their potential consequences. |
| Red | High risk | Signifies high risk. These risks need immediate attention and robust management strategies to avoid or eliminate them. Immediate action is necessary to prevent serious consequences. |
Prioritize Actions
Focus on the risks highlighted in red and yellow, as these pose the greatest threat to your organization. Allocate resources and implement measures to address these risks effectively. This prioritization ensures that you are tackling the most critical issues first.
Develop Risk Management Strategies
Create strategies to manage and mitigate the identified risks. This may involve developing contingency plans, increasing monitoring, or implementing new controls to reduce the likelihood or impact of the risks. Effective strategies will help you manage risks proactively and minimize their potential effects.
Benefits of Using a Risk Matrix
A risk matrix offers several advantages. It provides a clear visual representation of risks, making it easier to prioritize and address them. By categorizing risks into different levels, it helps organizations focus their efforts on the most critical areas, ensuring that resources are used efficiently. This clarity supports better decision-making and resource allocation.
Limitations to Consider
While useful, risk matrices have limitations. They can oversimplify complex risks and may not fully capture the nuances of each risk. The assessment process can be subjective, and the matrix does not account for changes in risk over time. Regular updates and supplementary risk management tools can help mitigate these issues, ensuring a more comprehensive risk management approach.
Conclusion
A risk matrix is a valuable tool for assessing and managing risks effectively. By understanding how to use it and recognizing its limitations, organizations can better prioritize their risk management efforts and protect themselves from potential threats.
Regularly updating the matrix and combining it with other risk management strategies will ensure a robust approach to managing risks. This balanced approach will help maintain resilience and safeguard against unforeseen challenges.
FAQs
What is a risk matrix?
A risk matrix is a tool used to assess and prioritize risks by plotting them on a grid based on their likelihood and impact.
How do you create a risk matrix?
To create a risk matrix, identify risks, evaluate their likelihood and impact, then plot them on a grid to prioritize them based on severity.
Why is a risk matrix useful?
A risk matrix helps organizations visually identify and prioritize risks, making it easier to focus on the most critical issues.
What are the limitations of a risk matrix?
A risk matrix can oversimplify complex risks and may rely on subjective assessments, requiring regular updates for accuracy.